Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) authentication
Ø ESISTONO 3 TIPI DI AUTENTICAZIONE
NONE (tipo 0)
SEMPLICE (tipo1)
MD5 (tipo 2)
Ø PER CONFIGURARE L’AUTENTICAZIONE E’ NECESSARIO ABILITARLA IN 2 PUNTI
1) SOTTO “ROUTER OSPF CONF” ABILITA L’AUTENTICAZIONE PER L’INTERA AREA à
router ospf 10
network 192.16.64.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 70.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0
area 0 authentication message-digest ß COMANDO 1
2) SOTTO “INTERFACE CONF”
interface Serial0
ip address 192.16.64.2 255.255.255.0
ip ospf message-digest-key 1 md5 kal ß COMANDO 2
note: OPZIONALMENTE SI PUO’ SOSTITUIRE
IL COMANDO 1 à area 0 authentication message-digest (SOTTO ROUTER OSPF, IL QUALE ABILITA L’AUTENTICAZIONE PER L’INTERA AREA) CON UN COMANDO à ip ospf authentication message-digest (SOTTO INTERFACE IL QUALE ABILITA L’AUTENTICAZIONE PER LA SOLA INTERFACCIA)
Ø OGNI VOLTA CHE SI CAMBIA L’AUTENTICAZIONE SI DEVE FARE IL CLEAR DEL PROCESSO OSPF
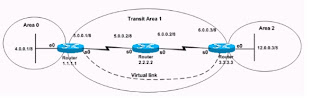
NEL CASO DELLA PRESENZA DI VIRTUAL LINK E’ IMPORTANTE CONSIDERARE IL RUOLO DEL VIRTUAL ABR à R3 (IL ROUTER INIZIALMENTE NON CONNESSO ALL’AREA 0)
R3 E’ IL ROUTER NON CONNESSO ALL’AREA 0 ESSO DIVENTA UN VIRTUAL ABR ED
HA BISOGNO PER L’AUTENTICAZIONE DI AVERE L’AREA 0 AUTHENTICATION ALL’INTERNO DI ROUTER CONFIGURATION. (usare SHOW IP OSPF VIRTUAL LINK per osservare lo stato UP ed il tipo di autenticazione usata)
R1
interface Ethernet0
ip ospf authentication-key cisco ß COMANDO 1
router ospf 2
area 0 authentication ß COMANDO 2
area 1 virtual-link 3.3.3.3 authentication-key cisco ß COMANDO 3
R3
interface Ethernet0
ip ospf authentication-key cisco ß COMANDO 1
router ospf 2
area 0 authentication message-digest ß COMANDO 2
area 1 virtual-link 1.1.1.1 message-digest-key 1 md5 cisco ß COMANDO 3
This document shows sample configurations for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) authentication which allows the flexibility to authenticate OSPF neighbors. You can enable authentication in OSPF in order to exchange routing update information in a secure manner. OSPF authentication can either be none (or null), simple, or MD5.
1. The authentication method "none" means that no authentication is used for OSPF and it is the default method.
2. With simple authentication, the password goes in clear-text over the network.
3. With MD5 authentication, the password does not pass over the network.
MD5 is a message-digest algorithm specified in RFC 1321. MD5 is considered the most secure OSPF authentication mode. When you configure authentication,
Ø you must configure an entire area with the same type of authentication.
Ø Starting with Cisco IOS® Software Release 12.0(8), authentication is supported on a per-interface basis
These are the three different types of authentication supported by OSPF.
· Null Authentication—This is also called Type 0 and it means no authentication information is included in the packet header. It is the default.
· Plain Text Authentication—This is also called Type 1 and it uses simple clear-text passwords.
· MD5 Authentication—This is also called Type 2 and it uses MD5 cryptographic passwords
Plain text authentication is used when devices within an area cannot support the more secure MD5 authentication. Plain text authentication leaves the internetwork vulnerable to a "sniffer attack," in which packets are captured by a protocol analyzer and the passwords can be read. However, it is useful when you perform OSPF reconfiguration, rather than for security. For example, separate passwords can be used on older and newer OSPF routers that share a common broadcast network to prevent them from talking to each
Nessun commento:
Posta un commento